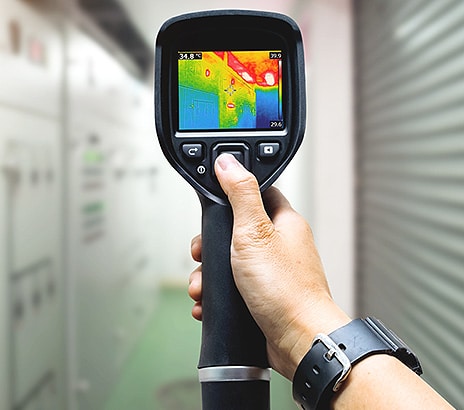
The technical team at Titan Power, together with Emerson Network Power, can deliver customized and comprehensive solutions for arc flash safety and compliance. As a leader in electrical testing, maintenance and engineering services, Titan Power is equipped to provide single-point solutions for every area affecting arc flash hazards. From arc flash calculations, personal protective equipment (PPE) recommendations and engineering support, to complete program development, implementation and training, Titan Power can help you ensure worker safety as well as regulatory compliance. Trust Titan Power to customize a solution to fit your needs.
Arc Flash is a serious hazard, with potentially devastating effects. Electrical hazards – specifically shock and arc flash – can result in serious injury or death to electrical workers. Obviously, the consequences of arc flash are devastating. Beyond the risk of personal injury and death, arc flashes can also lead to business disruption, costly damage to equipment and facilities, legal liability, increased insurance premiums, and hefty regulatory fines. Ensuring worker safety and meeting the challenges of new OSHA arc flash safety requirements can be a difficult task to accomplish.
Our technical team, together with Emerson Network Power, can help you select a single component, a combination of components, or an entire program to provide comprehensive arc flash solutions. These components include:
- Arc Flash Hazard Analysis
- Arc Flash Hazard Labeling Plan
- Site Review / Compliance Assessment
- Protective Scheme Design Review
- Single-Line Diagrams
- Short Circuit and Coordination Studies
- Preventive Maintenance and Program Assessment
- Electrical Safety Program Review / Development
- Training and Performance Evaluation
- Personal Protective Equipment Plan
- Optional Annual Re-certification
- Documentation
Benefits of implementing Arc Flash Solutions include:
- Ensure compliance with OSHA regulatory requirements
- Improve worker safety / Avoid accidents
- Reduce lost worker productivity
- Minimize costly fines and higher insurance costs
- Ensure optimum system performance, safety and efficiency
- Single access point solutions for every threat facing your critical facility